Currency trading has given rise to one of the biggest marketplaces with a daily turnover of more than $6 trillion. In the past, the marketplace was only accessible via large institutions, central banks, and investment firms. Technological advancements have opened it up, making it accessible even to remote parts of the world.
Contrary to perception, there is no central location for the trillion-dollar marketplace. The marketplace is decentralized in that there is no location through which transactions take place. Likewise, there is no central authority in control of what takes place in it.
Technology is at the center of everything that takes place in the trillion-dollar marketplace, making it possible for participants to deal with one another directly instead of operating from the centralized exchange.
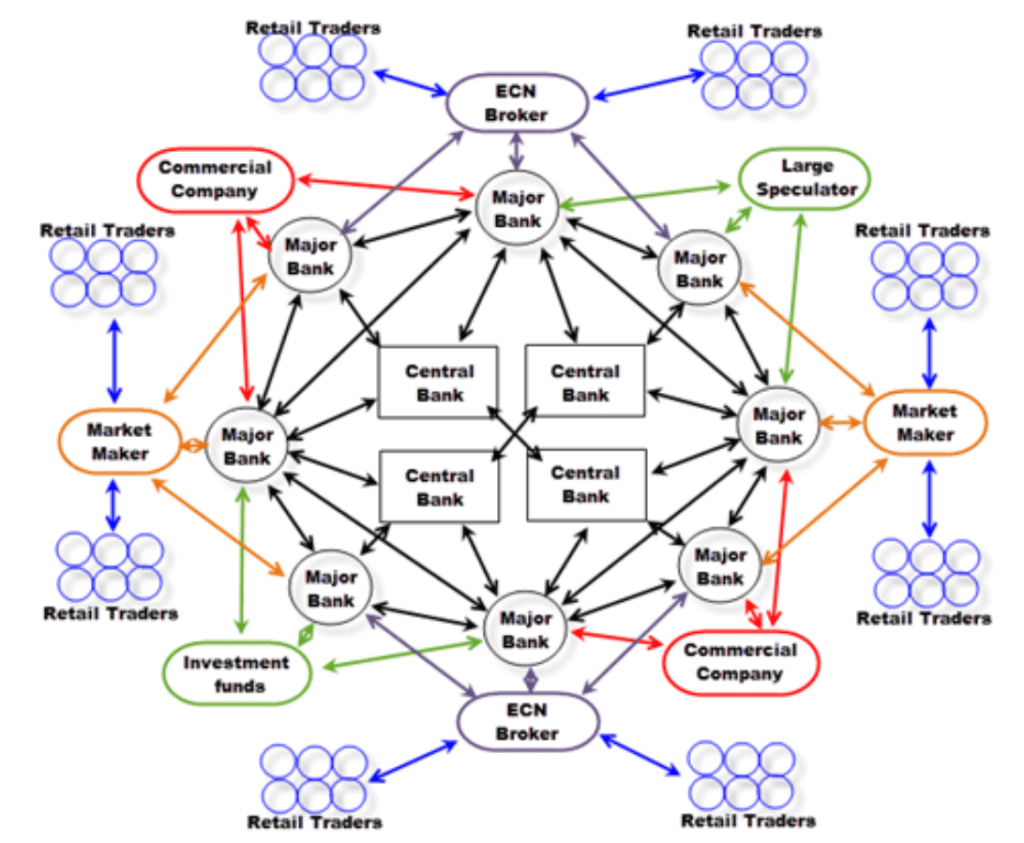
The forex market is enabled by various digital devices that communicate bid and ask prices in real-time. At the click of a button, one can buy or sell a preferred currency pair. Additionally, market participants don’t need to be in a given location to transact.
In addition to being decentralized, the currency trading business exists in different forms tailored to other people. It also operates 24 hours a day, unlike the stock market, and takes place in different channels worldwide.
It is considered over the counter, given that everything is carried out electronically within a network of banks and brokers. Therefore, the market is spread all over the world with no central body or authority in control. Participants in the marketplace determine who they want to trade with depending on price changes and trading conditions.
Where is it located
There is not a single central location that can claim to be home to the forex market. Being an electronic type of market, various spots in brokerage companies, central banks, and financial institutions offer support and enable transactions in the marketplace.
In contrast, the stock market has a central location in which trading activities occur. For instance, the New York Stock exchange and the London Stock Exchange account for most activities in the stock market.
Additionally, many trading platforms allow people worldwide to connect and exchange currencies. It is also a fast-paced market enabled by internet connections. In this case, one only needs a stable connection and a brokerage account to be able to access the market to buy and sell various currency pairs.
How it works without location
The lack of a central location is compensated by different sessions, which act as primary sources for different types of trades. The sessions are dominated by three major financial hubs of America, Asia, and Europe.
Trading activities in Japan mostly donate to the Asian session, thus often referred to as the Tokyo session. It is usually the first to come online, followed by the London session, which depicts trading activities when European markets are opened. The climax is the North America session, often referred to as the New York session.
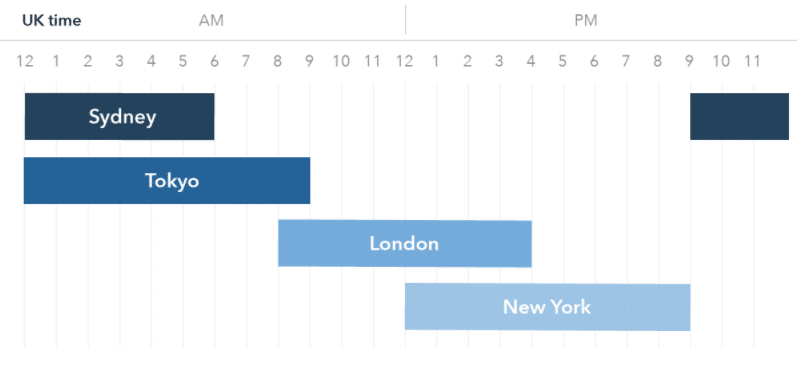
High liquidity and increased trading activities come into play whenever two sessions overlap. For instance, most traders pursue trading activities when the London and the New York sessions are running concurrently.
While there is not a single central location in which all the trading activities take place in the forex market, different locales are at the heart of the exchange activities. The four act as distributors, through which trading activities take place. They also play a crucial role in enhancing liquidity that enables buying and selling activities.
Retail forex brokers
Forex brokers play an essential role in the currency market, adding another layer of decentralization. They have opened up the marketplace to the smallest of traders by making it possible to trade regardless of where one is or the amount of capital one has.

Retail forex brokers play a pivotal part in providing trading platforms through which people can access the marketplace and place trades. By depositing a small amount of money, the brokers also offer leverage that allows market participants to place big positions that normally they would not be able to finance.
Given that the platforms can be accessed online, one only needs a stable internet to buy and sell various currency pairs regardless of location. In addition, the brokers allow people to access the market 24 hours, seven days a week.
Central banks
Central banks also add another layer of decentralization in the trillion-dollar market. The high amount of liquidity on offer allows these institutions to control their money supply, interest rates, and inflation. Central banks achieve this by buying and selling currencies to meet set targets as part of monetary policy.
Commercial businesses
Commercial businesses that carry out operations on the international scene are also key players in the forex market. From time to time, businesses must convert currencies to buy items or pay for services rendered.
For example, a company in Germany might have to convert its euro holdings to pay for goods and services rendered in the US. Similarly, a US company might have to alter its dollar holdings to yen to pay for goods bought in Japan.
Additionally, companies and businesses that deal with foreign suppliers and customers buy and sell currencies to hedge against significant rate fluctuations in the future.
Interbank market
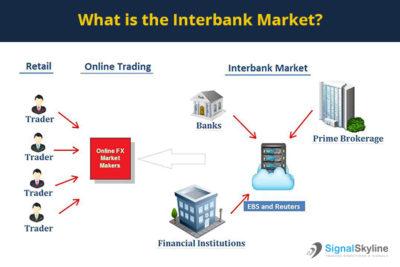
It is the largest portion of the forex market as it covers retail forex broker’s central banks and commercial businesses. All the above players turn to banks when looking to carry out currency exchange transactions.
Bottom Line
The forex market is highly decentralized as there is not a single central location where all transactions take place. The lack of a central location also means there is no central authority or body that regulates activities in buying and selling currencies.




