The manufacturing and services sectors are the biggest employers in most countries. Therefore, forex traders, policymakers, and investors typically pay close attention to these sectors’ performance to gauge the outlook of the economy. In this article, we will look at the manufacturing and services PMI data and how you can apply them in forex trading.
What are PMI numbers?
The Purchasers Manufacturing Index (PMI) is the economic release that measures the level of activities by companies in several sectors. In addition to manufacturing and services, agencies also publish other types of PMIs like construction and composite.
PMI numbers are collected by several research agencies globally, but the most popular one is IHS Markit. Markit is a global company that is being acquired by S&P Global in a 33 billion pounds deal. The company partners with local agencies, typically banks, to collect data from companies. These numbers are then presented every month. Other organizations that publish the PMIs are the Institute of Supply Management (ISM) in the United States and China Logistics.
The PMI number usually measures the performance of a sector by looking at the actions of purchasing managers. The idea behind this is relatively simple. In a strong economy, these managers will usually be relatively busy as they buy more.
Therefore, a closer look at these PMI numbers can give you more details about the state of the economy. Every month, Markit and its partners usually publish two PMIs. The first one, known as the flash PMI, is usually released in the final week of the month. The final figure is released in the first week of the next month. The manufacturing PMI usually comes out first, followed by the services and composite PMI two days after.
Types of PMI data
There are three main types of PMI data. These are:
- Manufacturing PMI – This PMI looks at the performance of the manufacturing sector. While the sector is an important part, it represents a relatively small part of the economy.
- Services PMI – This data measures the performance of the services sector, which includes businesses like hotels, restaurants, and transport.
- Composite PMI – This data combines several indices of both the manufacturing and services sectors.
- Construction PMI – This PMI looks at the performance of the construction sector. It looks at the civil construction and housing sectors.
Components of the PMI data
In general, the PMI is survey data where the researchers asked several questions about their activities. These questions are mostly on several key aspects of business, including:
- Order inflows – This figure looks at the trends in orders from customers. In a strong economy, companies will typically record strong order inflows.
- Business confidence – The data looks at how confident companies are. This is notable since highly confident companies will mostly hire more people and boost their spending.
- Cost of doing business – The cost of doing business looks at the amount of money that companies are paying for inputs. A higher cost of doing business is a sign of more demand, which is a positive sign for the economy.
- Employment – This component of the PMI looks at the levels of employment across the respective sectors. In a strong economy, companies will have an incentive to add workers.
- Supply lead times – This data looks at the time that a company takes from ordering a product to the actual delivery. In a strong economy, these lead times will likely be longer.
Meaning of manufacturing and services PMIs
The manufacturing and services PMI number usually ranges from 0 to 100. The most important number in this is usually 50. If a sector’s PMI is above 50, it is usually a sign that business output is growing. Therefore, if the number falls from 55 to 53, the interpretation is that the sector expanded at a slower pace.
On the other hand, a PMI figure of 49.9 and below is usually a sign that the sector’s output is lagging. For example, the chart below shows that the US manufacturing PMI declined to a record low at the start of the Covid-19 pandemic. At the time, most manufacturers were forced to shut down their operations as lockdown measures came into place. The situation changed as the country started to reopen.
US manufacturing PMI
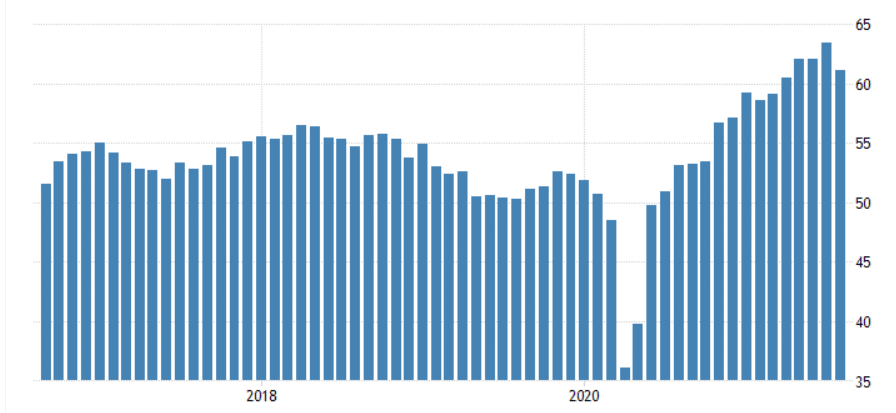
While manufacturing and services are important, in most cases, only those of a few countries have an impact on the Forex market. Those that you should focus on are from the United Kingdom, China, United States, and the Eurozone. The rest rarely have an impact on currency pairs.
How to trade PMI data
There are several things you need to do to trade PMIs well. First, you need to know when these numbers are coming out. Therefore, you should use the economic calendar routinely. A calendar is an important tool that provides a schedule on when these numbers will come out. In my experience, I have found out that the flash PMI numbers that come out near the end of the month are better because they are usually not all that different from the final report.
Second, you need to understand the trend of these sectors by looking at the specific charts such as the one shown above. Looking at this chart will give you more details about the state of the sectors.
Finally, a simple way to trade these numbers is to set bracket orders. A bracket order is one that has both a buy-stop and a sell-stop. These two trades are then protected using a stop loss and a take profit.
Still, in the past few months, the impacts of these PMI numbers on volatility have been relatively muted. This is mostly because of forward guidance given by central banks. In it, the bank tends to tell investors about its actions in advance. As such, investors tend to focus on hard data like employment and inflation.
Summary
Manufacturing and services PMI are important economic numbers that provide forex traders with details about the state of the economy. In this article, we have looked at how these numbers work, who provides them, how to interpret them, and how you can use them in trading.




