Inflation is an important economic data in the financial market. Indeed, it is one of the most closely watched figures by investors and traders. In this article, we will look at what inflation is, why it matters, and some of the key inflation gauges to watch in forex trading.
What is inflation?
Inflation refers to the overall change in the prices of items in an economy. For example, if the price of a loaf of bread that used to sell for $10 in 2020 rises to $15 in 2021, it means that there is inflation in the market. If, on the other hand, the price falls from $10 in 2020 to $7 in 2021, it means that bread experienced a deflation.
Why inflation matters in forex
Inflation is important in forex because it has an impact on the underlying currency. For example, if you had $100 in 2020, it means that you could have bought ten loaves of bread when the price was at $100. With the same amount in 2021, the $100, you could have bought less than seven loaves of bread with your $100.
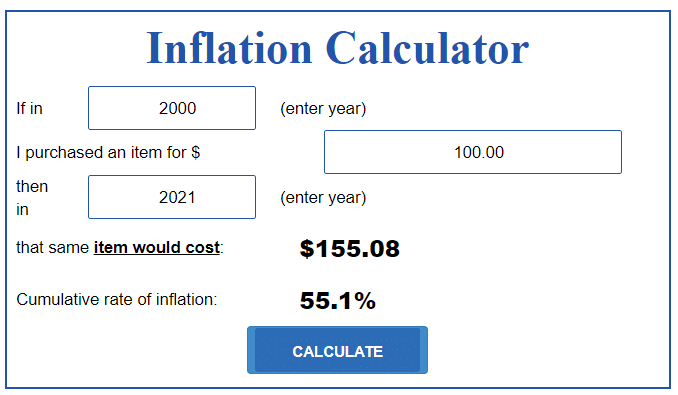
The chart below shows that if you purchased an item for $100 in the year 2000, the same amount would cost you $155 in 2021. In other words, the value of US dollars keeps falling in the long term.
Inflation calculator
Inflation also matters in forex because it forms part of the Federal Reserve dual mandate. The Fed is given the mandate to ensure that inflation remains stable and that the country has the lowest unemployment rate.
It does this through its special role of regulating the money supply, setting interest rates, and using tools like quantitative easing. In theory, when inflation rises above the Fed’s target of 2.0%, the Fed should tighten monetary policy by hiking interest rates. By doing so, the regulator limits the supply of money and puts inflation under pressure. When the dollar supply falls, the currency’s value tends to rise as well.
Similarly, when inflation falls, the Fed tends to lower interest rates and, at times, offer quantitative easing. This leads to more supply of dollars and boosts inflation. So, let us look at the key inflation gauges to watch in forex.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
Consumer spending is one of the biggest factors impacting the American economy. Therefore, the CPI is the most widely-used measure of inflation since it considers the price change of all items like furniture, food and beverage, cigarettes, cars, and household goods of urban consumers. The CPI data is published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) every second week of the month.
The BLS calculates the CPI by using data from the Census Bureau to select the best urban areas to consider. After this, the bureau uses a sample of about 14,500 families to know where they buy most of their items. They then collect the prices of key items and consider their change from their previous month and the same month the year before.
The CPI data is accompanied by the core CPI data. Core CPI is a number that considers the prices of all categories, but it excludes those of food and energy. The two sectors are excluded because of how volatile they are.
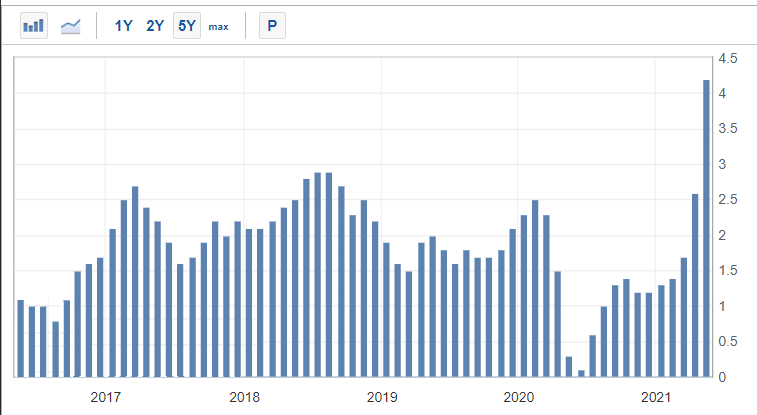
The chart above shows the overall trend of US CPI data from 2016 to April 2020. As you can see, the CPI dropped during the pandemic and then started to rise.
Producer Price Index (PPI)
The PPI is another popular gauge of inflation in the United States. The data typically comes a few days after the Bureau of Labour Statistics publishes the CPI data.
While the CPI focuses on consumers, the PPI focuses on domestic producers. It measures the average changes in selling prices that are received by domestic producers. The index is calculated by looking at the prices of hundreds of industries and more than 3,700 commodity price indexes, and over 600 indexes for aggregate price changes.
The PPI is often more sensitive to the prices of commodity prices like lumber, copper, and crude oil. The number is also important because the prices paid by domestic producers are translated to what they charge their customers – the retail sector.
US PPI since 2016
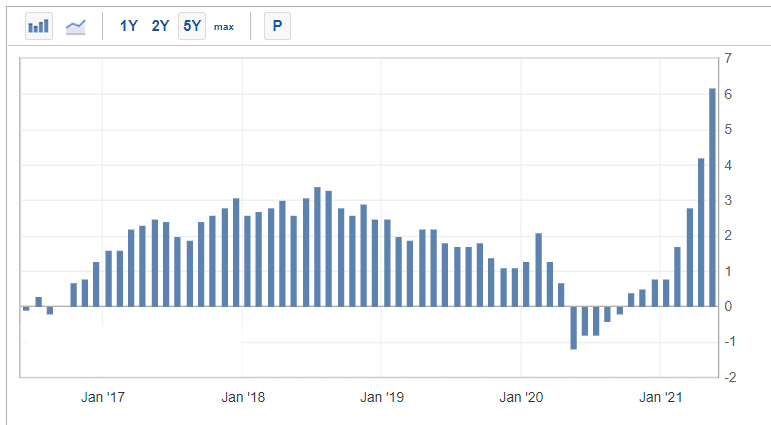
The PPI looks broadly at the prices of key items, while the core PPI excludes the volatile products that affect the prices of items. The chart below the US PPI data since 2016.
Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE)
The PCE is an important gauge of inflation in the United States. It is the Fed’s favorite measure of inflation. The data measures the goods and services that are purchased by the private sector. It also takes into consideration the personal income and personal expenses numbers.
In most cases, the PCE readings rise when the economy is doing well and fall when it is going through challenges.
PCE chart
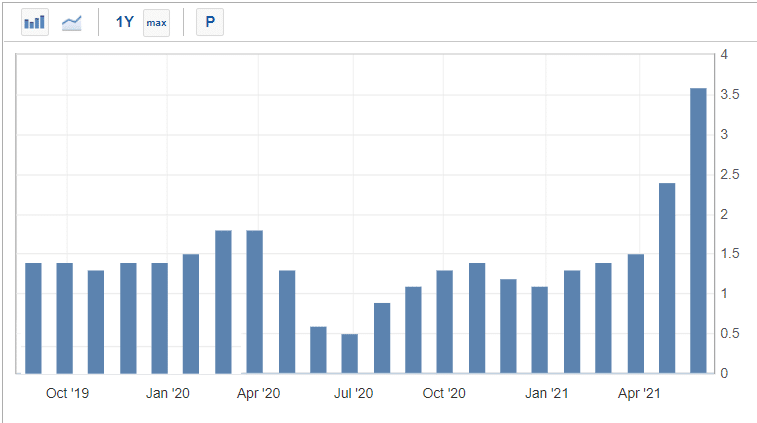
A key difference between the CPI and PCE is that the latter includes more numbers. For example, if you go to a hospital and pay a copay and the insurance company pays the rest, the PCE will capture both. The CPI looks at what you pay at the hospital. The chart above shows the year-on-year increase in PCE.
Consumer confidence
Another indirect measure of inflation in the United States is consumer confidence. These are numbers that measure the overall sentiment of Americans. Ideally, when Americans are more confident about their future, they tend to spend more money on electronics, furniture, clothing, accessories, housing, and other items. This, in turn, leads to higher prices as demand rises.
On the other hand, when Americans are not confident about their future, they tend to save more, which depresses the prices of items.
US consumer confidence data
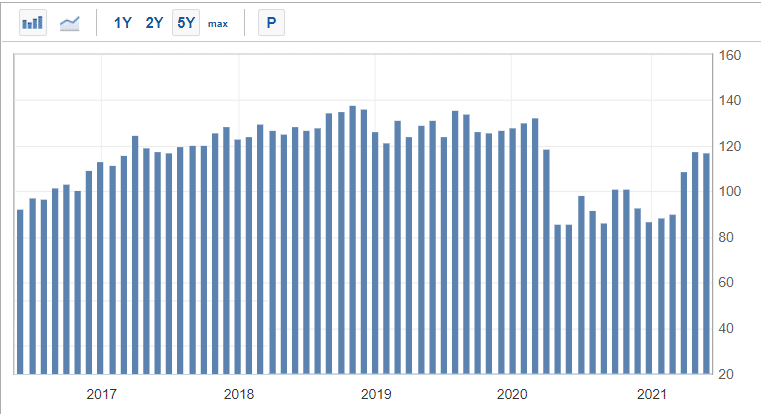
In the United States, consumer confidence data comes from several organizations like the Conference Board and the University of Michigan. The chart above shows the recent CB consumer confidence data.
Summary
Inflation is an important data of fundamental analysis in forex trading. This is because it has a role in the country’s monetary policy. In this article, we have looked at what inflation is and some of the key gauges that you can use to forecast the country’s inflation rate.




