The INR/USD currency pair is fast emerging as a popular currency pair in the forex market. In this article, we take a look at how well the INR/USD pair exchange rate is tied to India’s economic growth. Given the growing business market, the INR/USD pair is quickly becoming an attractive opportunity for forex traders to invest.
INR/USD and the Dollar-denominated debt
INR, which stands for Indian Rupee, is India’s currency, while USD is the currency of the United States. INR/USD is a minor forex currency pair as it is not as heavily traded as other currency pairs. As it is expressed in terms of the US dollar, any strengthening or weakening has a direct effect on the INR/USD exchange rate.
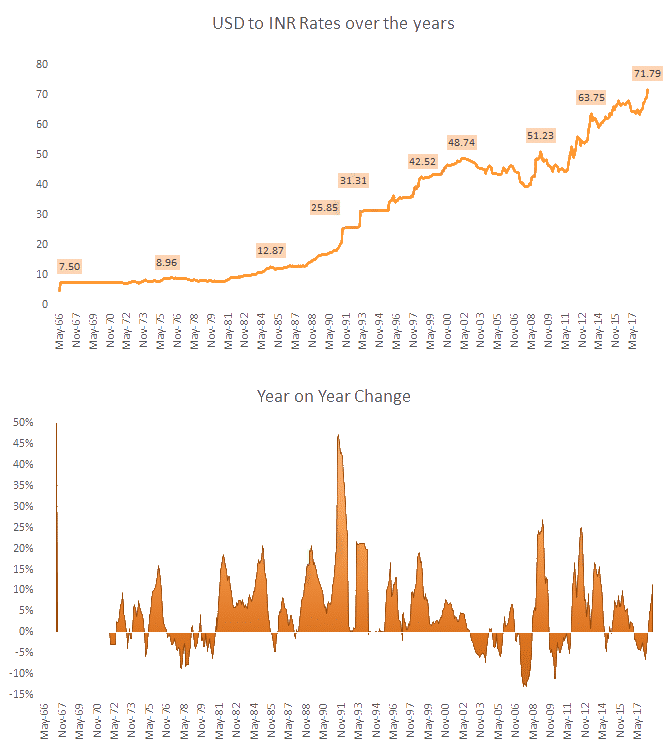
If the USD strengthens against the Yen, Pound, and the Euro, it will appreciate against the INR as well. As can be seen from the chart below, there has been a constant rise in the INR/USD exchange rate over the years. In the past five years, the INR has depreciated by more than 13% against the dollar.
The chief reason for this is that most of India’s foreign debt and trade is denominated in the USD. As such, any increase in the strength of the dollar index is translated automatically into the INR/USD exchange rate by the same degree.
Indian economy: South East growth path
Of late, India’s economic success has made South Asia the world’s fastest-growing region. However, its opportunities for further growth do not come without its challenges.
India has the seventh-largest economy in the world and is growing faster than any other big economy, save for China. It is projected that India will have the second-largest economy by the year 2050. The new Goods and Services Tax system has brought the 29 states of India under a common market. This is expected to boost the efficiency and growth of India. Plus, the new tax collection system is displaying promising early signs.
Furthermore, India and China’s population disparity is going to change direction with India set to overtake China by 2024. This, coupled with the fact that India has a younger working population, certainly gives India a substantial competitive edge over China in the years to come.
India’s growing economic clout is also being translated into a push for ‘soft power’ through the building up of diplomatic ties and cultural influence. The competition with China in the South Asian region has been brought sharply into focus as India looks to reject Chinese influence and become self-sufficient.
What moves INR/USD
Let us move forward and take a brief look at the various factors that move the INR/USD currency pair.
1. INR forward market hedging
INR Forward market hedging is quite large in India. It is an over the counter market since there is no trade being done on a regular exchange. Most of the time, oil companies, importers, and foreign currency borrowers hedge their exposures in dollar terms. But, as hedging takes away a huge percentage of the profits, most entities tend to retain a portion of their dollar exposures.
When the rupee gets volatile, importers and other players head to the bank and hedge their dollar exposure. As such, the demand for dollar goes up, and the INR in relation to the USD further weakens. Therefore, any loss made on the dollar due to a weak INR can be compensated by the futures on the INR/USD.
2. India Central Bank Interest rate
Whenever the government has committed to maintaining fiscal discipline, INR has witnessed strength. On the other hand, when expenditures go unchecked, the fiscal and revenue deficits feel the brunt of the impact.
For instance, in 2013, India’s revenue deficit reached a high of 5% that resulted in the INR crashing sharply against the dollar. The pressure on the INR is immediately felt as a result of deteriorations in key macroeconomic elements. Furthermore, the role of India’s central bank, the Reserve Bank of India, has had a substantial impact on the currency value.
Whenever interest rates in India are adjusted, there is a direct impact on the INR/USD exchange rate. When they are hiked, investors and other players prefer investing in the bonds as the spread is much more attractive over the US bonds. Naturally, a strong rupee is linked with higher interest rates and a weak rupee with lower interest rates.
Furthermore, determining whether a currency is overvalued or undervalued is a useful measure. This is reflected by the Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER). Normally, higher inflation ought to lead to depreciation. However, this has not been the case with INR. Even though it has witnessed higher inflation compared to other developed nations, it has been riding on higher foreign direct investments (FDI) and foreign institutional investors (FII).
3. GDP growth expectation
There has been a positive correlation between the Stock market growth and appreciation of INR. The stock market and the INR are directly as well as indirectly affected by various factors. These include the following:
- Monetary policies
- Governance
- Trade deficit/surplus
- FII inflows and outflows
- Forex reserves
- Outlook for the economy
Out of all these factors, perhaps there is none more positively correlated to INR and the stock market than FII flows. Demand for the INR goes up when FIIs invest in the Indian market, leading to a strong market, which results in a better outlook attracting further FIIs. Such a cycle is very beneficial but the reverse is also a possibility.
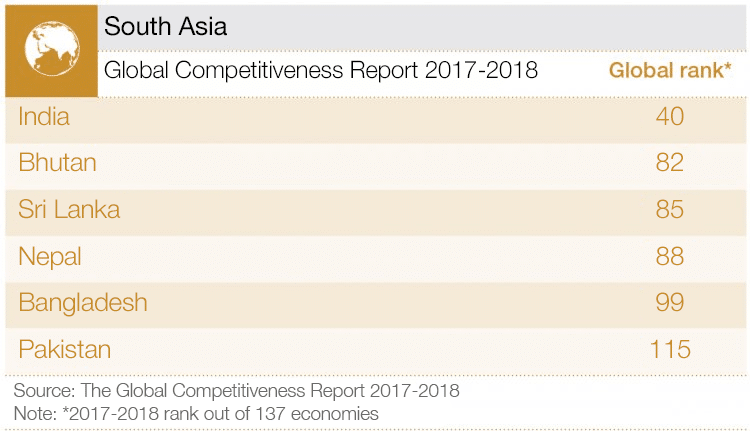
In the Global Competitive Index Report, India is currently on the 40th position for efficient public spending, a marker that is perceived to usher a stronger GDP growth. Despite a dip in the recent GDP growth figures, India still remains a robust economy that is projected to bounce back on the basis of FIIs, a stronger domestic market, and a committed fiscal discipline.
The Conclusion
Notwithstanding the current contraction of the Indian economy precipitated by the pandemic, some various factors and indicators highlight the renewed interest in the INR. The INR/USD currency pair is dependent very much on the performance and outlook of the Indian economy.
Factors such as FIIs, interest rates, forward market hedging, and monetary policies, directly and indirectly, affect the INR, leading to a change in the INR/USD exchange rate. Those looking to trade this minor currency pair would do well to pay attention to such markers, especially the stock market, which has a major influence on the changing values of the INR.