Wondering what Gaps and Slippages mean? Gaps and Slippage make up a vital part of forex trading and having a concrete understanding of the concept is crucial to make profitable trades. Experienced traders keep a constant track of gaps and slippage to maximize their gains. Read further to understand what gaps and slippage are, why they are important to you, and how you can trade effectively by using them in your trading strategy.
Gap vs Slippage
A Gap refers to a market situation where an interval occurs in the price line. A gap is commonly caused by the lack of any prominent trading actions – little to no trading takes place during a gap. This makes it difficult to predict or foresee gaps. Price lines are known to witness gaps during both uptrends and downtrends. Traders believe gaps to be catalyzed by unexpected events or any piece of news with the potential to disrupt the market equilibrium. Sometimes gaps can also be caused by sudden internal fundamental changes in the pricing of an asset.
It is important to keep track of gaps as traders can make use of these intervals to get a jumpstart on major price fluctuations. By making use of strong technical indicators and effective market analysis, traders can use gaps efficiently to drive their trading strategy. Various types of gaps are employed to analyze the nature of the upcoming trend, the speed of the trend, and the end of a trend.
The chart depicts an instance of a gap in the forex market. Towards the end of a large red candle, the gap occurs in the price line. This is then followed by a bearish candle with a relatively shorter body.
Another term associated closely with market gaps is Slippage. Slippage occurs when the price at which the asset order was initiated differs from the price at which it was completed. Slippage usually occurs in a highly volatile market. It can also occur when the stop loss closes an order at a price different from the one set initially. Slippage includes both increment and decrement in the initial price and does not always spell a loss for the traders. Traders classify slippage as positive, negative, or no slippage based on the gain or loss incurred due to the price difference.
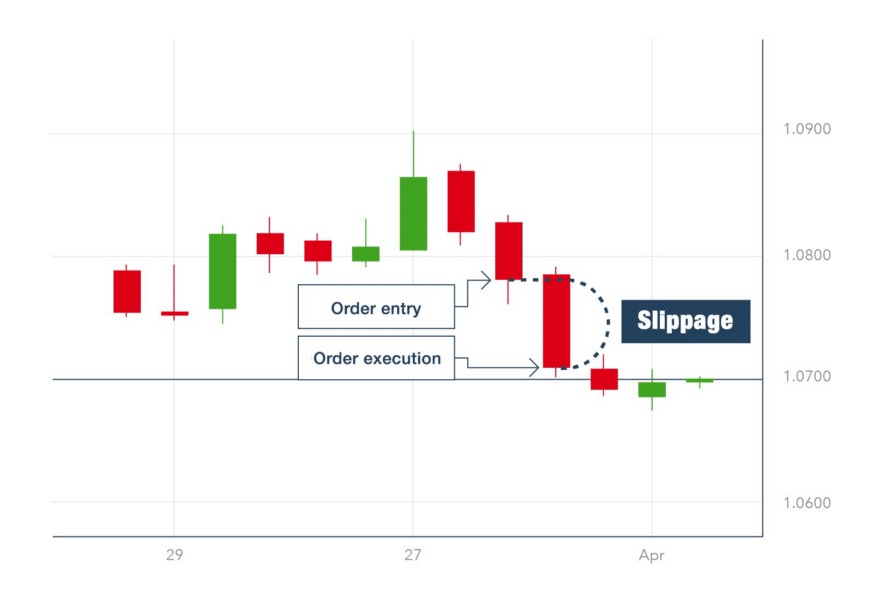
Examples of Slippage:
Assume that you placed an order at 1.30,
- The order gets executed at 1.30. In such a case, there is no slippage in the order.
- The order gets executed at 1.33. In such a case, there is negative slippage in the order.
- The order gets executed at 1.28. In such a case, there is positive slippage in the order.
Using Gaps while Trading for Your Advantage
For trading gaps in the market, it is important to understand the types of gaps that can occur and how to use them while trading.
There are 5 major types of gaps that can occur in the market. They are –
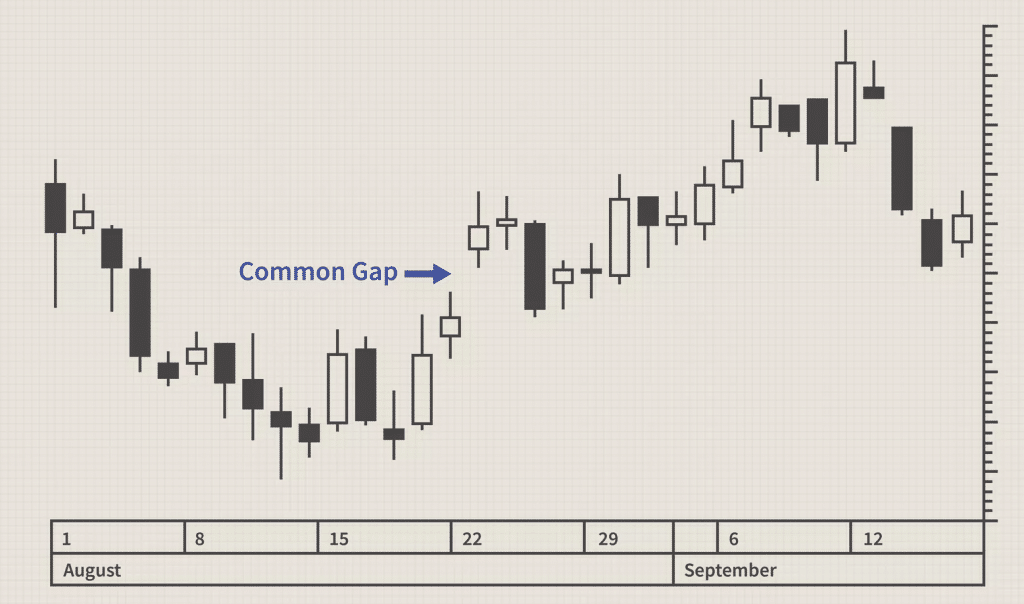
- Common Gaps: Also known as area gaps or trading gaps, Common Gaps occur due to the normal price fluctuations in the market. They occur quite frequently in the market and are not caused by any uncertainties or unexpected events. The magnitude of common gaps is quite small – they do not offer a huge margin of price difference before and after the gap. Traders cannot employ common gaps for major price advantages or use them conveniently for market analysis. It is very common to see these gaps when the forex market is closed.
- Breakaway Gaps: Initiated primarily by global news or international disruptions, Breakaway gaps are caused during the occurrence of chart patterns or strong trends. It is also typical to see them during a range. A range is a movement during which the prices stay with a small value of high and low and do not fluctuate above or below the range. It is different from a trend where the prices keep rising or falling in one direction. When the price line transforms from a range to a trend, it can be brought about by a breakaway gap. A breakaway sustains for a very long time. After the gap, the same trend starts continuing which was observed during the breakaway. Breakaway gaps bring about a major rise in the asset’s volume.
- Runaway Gaps: Such gaps occur in the middle of ongoing trends. Due to a steady trend, more and more traders are inclined to participate in the movement. As more traders take part is an ongoing trend, it leads to a runaway gap in between. It is an indicator of the strength and momentum of the existing trend. Runaway gaps also lead to a rise in the asset’s volume.
- Island Reversal Gaps: It is a reversal gap during which the ongoing trend is followed by a gap that moves sideways and then a trend in the reverse direction. It appears like an island on the chart, which is how it gets its name.
- Exhaustion Gaps: You will notice these gaps towards the finish of trends, mostly following a huge price change. Traders use them to make forecasts about when a trend is about to end. The trading volume fluctuates heavily during an exhaustion gap, it can turn very low or very high depending on the market situations before the gap. Higher volume bars after low bars indicates trend reversals after the exhaustion gap.
Bottom line
Generally, gaps persist for a short period of time. It is critical for traders to keep a constant track of the price chart to keep an eye for any gaps. Traders also need to be able to differentiate between the different types of gaps that occur to be able to optimise their profits during such a time. Gaps, when used efficiently, can help traders form a complete market analysis and proper trading strategies. Keep in mind that gaps are a risky and highly fluctuating aspect of trading. Traders always use a combination of technical and fundamental indicators to read market gaps.