Fundamental analysis refers to the process of using macroeconomic data and news events to predict the future direction of a currency. It is the opposite of technical analysis, which uses indicators like the Parabolic SAR and MACD to analyze currency pairs. In this article, we will look at the top 5 fundamental analysis indicators you should always use in forex trading.
Inflation
Inflation is probably the most important fundamental indicator in forex. As you will note below, most other fundamental or economic indicators have an impact on inflation. For starters, inflation refers to the process where the prices of items rise over time. As prices rise, the value of the currency declines. For example, $100 in 1950 bought more items than it does today.
Inflation is watched closely by forex traders because of its role in interest rates. When inflation rises so fast, central banks typically respond by raising interest rates or tightening the monetary policy. On the other hand, when inflation falls, they lower rates in a bid to incentivize people to spend money. As they spend, inflation rises, forcing the central bank to hike rates in a bid to tame runaway inflation.
Inflation is typically watched through the consumer price index (CPI). This is an important number that shows how prices of goods changed in a given month. It looks at most items that consumers buy, like clothing, food and energy, and other bills, and see how they changed. In most developed countries like the US and Europe, the central banks prefer the CPI holding at 2.0%.
Another closely-watched measure is the producer price index (PPI). This gauge targets local producers and the prices they pay for goods and services.
Employment
Employment is another important fundamental analysis indicator used in forex. Ideally, an economy that is doing well will have more people in the workforce. It will have fewer people without work, and wages will keep rising.
Countries publish their employment numbers periodically. In the United States and Canada, the statistics agencies publish the jobs data every first Friday of the month. Countries like the UK and Australia also publish their employment data every month.
Traders watch several things when a country publishes its jobs numbers:
- Job additions. This refers to the total number of jobs that have been added in a given month. More is better.
- Participation rate. This is a gauge of the number of people of working age that are working or looking for work.
- Unemployment rate. This is a number that shows the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed but is actively looking for work. A lower rate is better.
- Wages. This is a number that measures the rise of wages in an economy. When wages rise, they buy more, leading to more employment.
- Working hours. This figure refers to the average number of hours worked. If wages and the number of hours worked rise, it will lead to more economic output.
Employment numbers have an impact on inflation. In theory, the rate of inflation tends to rise when the unemployment rate is low. This concept is known as the Phillips curve in economics.
Retail sales
The retail sector is the leading employer in most countries globally. It employs people in supermarkets, hotels, and other retail outlets. At the same time, it supports many industries like fast-moving consumer goods, furniture, and electronics. Therefore, the retail sales numbers that are published periodically are important fundamental analysis indicators.
In an economy that is doing well, the volume of retail sales will keep rising. Furthermore, people have the resources to spend on takeout food, electronics, and other products. The opposite is true. When the economy is suffering, the volume of retail sales will drop. For example, as shown below, the volume of retail sales in the US crashed in 2020 during the pandemic. It then rebounded after the government provided stimulus checks.
US retail sales
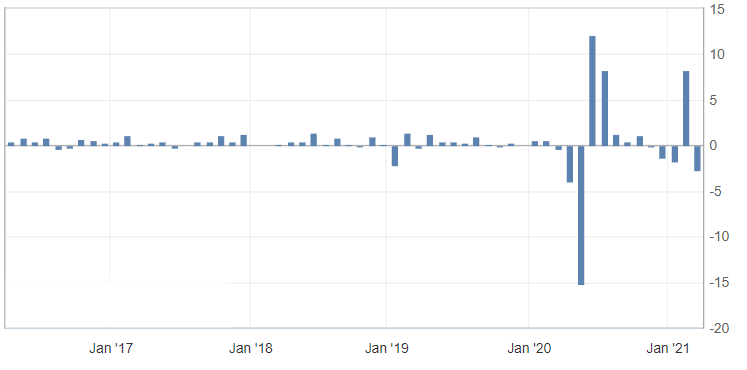
Retail sales, too, have an impact on inflation. When sales rise fast, it means that there is high demand. When demand increases, it leads to higher prices in the marketplace.
Manufacturing and services PMIs
The services sector is the leading employer in most countries. In the UK, it employs more than 60% of the entire population. While the manufacturing sector does not employ many people in Western countries these days, it helps to support the services sector.
Therefore, traders pay close attention to the manufacturing and services PMI numbers that are published every month. The PMIs are calculated by interviewing purchasing managers in companies about their recent activity. The surveys are mostly carried out by IHS Markit in collaboration with local organizations like banks. It looks at their order flow, hiring activity, optimism, and supplier delivery times.
The PMI figure ranges between zero and 100. Any figure above 50 is a sign that the sector is doing well. A reading below 50 sends a signal that the sector is struggling. Forex traders use the PMI numbers to gauge the health of a country.
Interest rates
The most important fundamental analysis indicator is interest rates. When conducting its rate decision, the monetary policy committee of a bank sits down and looks at all economic numbers. Specifically, it looks at the progress on employment and inflation to determine the rate policy.
If the unemployment rate is low and inflation is rising, there is a possibility that it will either raise rates or sound a bit hawkish. Similarly, if inflation is low and the unemployment rate is rising, the bank will likely sound dovish. In the United States, the Federal Reserve prefers it when the unemployment rate is below 5%, and the inflation rate is around 2%.
Final thoughts
Having a good understanding of fundamental analysis can help you become a better trader. In this article, we have looked at the most important fundamental analysis indicators that you will find in the economic calendar. Other indicators that we have not looked at are industrial production, current account, and the latest news.




