Inflation is an important economic data that is followed closely by forex traders and policymakers globally. It is also an essential gauge of the performance of the economy. In this article, we will look at what inflation is and how you can use this data effectively in the financial market.
What is inflation?
Inflation refers to a situation where the cost of items in a country rises. For example, if the price of a food item rises from $2 to $2.5, it can be said that inflation has happened. While the issue may seem trivial, in reality, it has a major impact on currencies and policy directions.
Ideally, there are three price-related things that can happen in an economy. First, the prices of items could rise, which is known as inflation. Second, the prices can decline for a long period. This is known as deflation. Third, inflation can remain the same for a longer period of time.
There are other concepts of inflation that traders look at closely. The most feared are hyperinflation and stagflation. Hyperinflation is a period where consumer and producer prices rise at exponential levels, as it happened in Zimbabwe. Stagflation, on the other hand, is a situation where there are high inflation and a high unemployment rate.
Inflation impact on currencies
A commonly asked question is how inflation affects a currency. In fact, of all things that have an impact on currencies, inflation comes first. For example, if you have $1,000 and a loaf of bread costs $20, it means that you can buy 50 loaves today.
However, if the price rises to $23 in a year, it means that your $1,000 will buy you just 43 loaves during this time. In other words, when there is high inflation, it means that your cash will buy a smaller number of items.
On the other hand, in a period of deflation, it means that your money will buy more items. In the above example, if the price of a loaf of bread drops to $18, it means that you can buy 55 pieces.
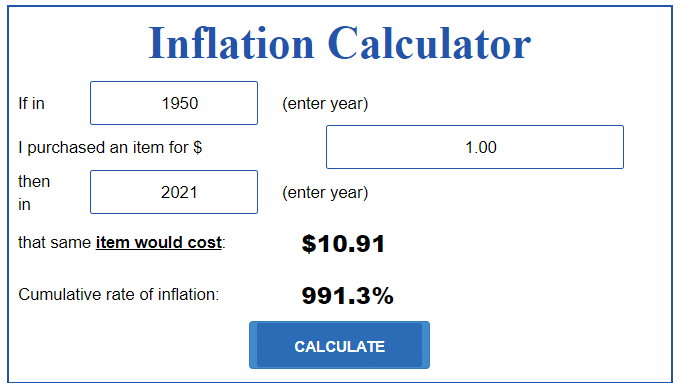
In the past, the US dollar has lost value. What a dollar bought people 50 years ago cannot buy the same item today. As shown below, $1 in 1950 is today (2021) worth about $10 because of inflation.
US inflation calculator
A more serious situation is known as hyperinflation. When it happens, the currency usually loses value, as it happened in Zimbabwe. Today, the country does not have a local currency.
Why inflation matters to forex traders
Forex traders pay close attention to inflation for several reasons. The most important is that consumer prices have an impact on the decisions by central banks. Indeed, the dual mandate of the central bank is to ensure that prices remain stable and that the unemployment rate remains low.
To achieve the dual mandate, a central bank has several tools, with the most popular ones being interest rates and quantitative easing. In most Western countries, central banks work to push inflation to 2%. Therefore, if inflation moves above this target, the bank will start hiking interest rates in a bid to curb the fast inflation pace.
At the same time, when there is an economic crisis, inflation will typically fall. For example, at the height of the coronavirus pandemic, inflation in the United States declined to almost zero. In this period, the central bank will lower interest rates in a bid to spur spending. During the pandemic, the Fed and other global central banks slashed rates.
Therefore, traders pay close attention to inflation data that are released every month in a bid to predict what the central bank will do.
Top inflation data watched by forex traders
Forex traders watch several economic numbers in the economic calendar to determine the inflation issues. These are listed below.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
The CPI is the most common measure of inflation in most countries. The data is released every month in most countries. In the United States, it is published by the Bureau of Labour Statistics, while in the UK and the EU, it is published by the Office of National Statistics (ONS) and Eurostat, respectively.
The CPI looks at the change of prices in a given period. It looks at the price of most items and how the prices changed. Some of the most important components of the CPI index are food, electricity, clothing, and energy.
In addition to the CPI, the agencies also release the so-called core CPI. This is similar to the CPI data but it excludes items like food and energy because of their volatility.
Producer Price Index (PPI)
The producer price index, also known as the factory-gate price index, is a measure of inflation that looks at the selling prices that are received by local producers for their inputs. The difference between PPI and CPI is that they focus on corporates and households, respectively. When the PPI rises, it sends a signal that other prices too will rise.
Unemployment rate
The overall unemployment rate is an indirect measure of inflation. That’s because of the special relationship that exists between the unemployment rate and inflation. It is known as Philip’s curve. The theory behind it says that inflation rises when the unemployment rate falls, and vice versa. For one, people tend to buy more when they are employed. Therefore, when the unemployment rate falls, it sends a signal that the central bank will hike rates to cool the economy.
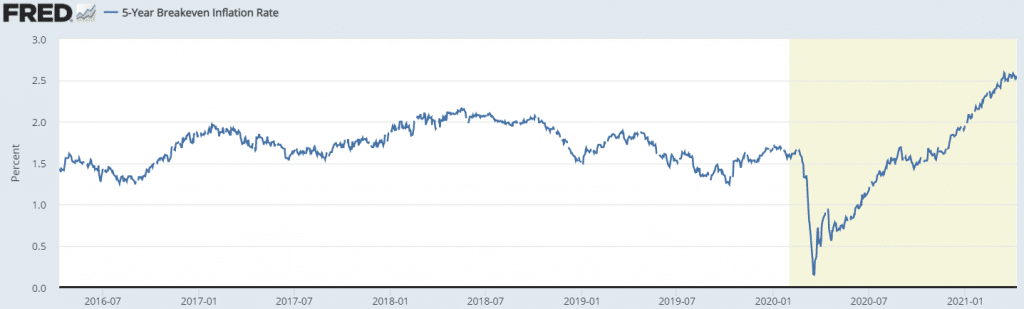
There are other measures that forex traders look at when using inflation to trade. These are the personal income and expenses, retail sales, wage growth, and the 5-year breakeven inflation rate. The latter is used to show what the market expects the rate of inflation to be in five years. The chart below from FRED shows how the chart looks like.
Summary
As a forex trader, there are many data points that you should pay attention to. Some of these numbers are employment, industrial production, retail sales, and manufacturing and services PMIs. Still, inflation is the most important. Therefore, as a trader, you should always use the economic calendar to figure out the current inflation and what it means for the future of interest rates.